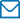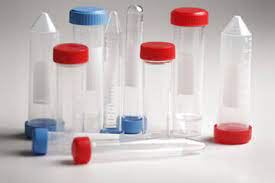
Centrifuge tubes are an essential tool in scientific research and medical laboratories. They are used to separate materials based on their density by spinning the tube at high speeds, causing the heavier components to settle at the bottom of the tube. In this article, we will provide an ultimate guide to centrifuge tubes, including the types available, their uses in various scientific and medical applications, and best practices for handling and storing them.
Types of Centrifuge Tubes: Centrifuge tubes are available in a variety of sizes, materials, and designs. The most common types of centrifuge tubes include:
- Polypropylene Tubes: These are the most common type of centrifuge tubes and are made of durable polypropylene plastic. They are available in different sizes ranging from 0.2 mL to 50 mL and are ideal for general-purpose centrifugation applications.
- Glass Tubes: Glass tubes are a popular alternative to polypropylene tubes as they are more resistant to chemical damage and can be sterilized using high-temperature methods. They are also suitable for applications that require optical clarity, such as microscopy.
- Microcentrifuge Tubes: Microcentrifuge tubes are small, cylindrical tubes designed for use in microcentrifuges. They typically hold between 0.2 mL and 2 mL of liquid and are ideal for applications that require low sample volumes, such as PCR amplification.
- Conical Tubes: Conical tubes have a conical shape that allows for easy separation of samples. They are commonly used for centrifugation applications that require the separation of a solid or semi-solid material from a liquid.
- PCR Tubes: PCR tubes are specialized tubes designed for use in polymerase chain reaction (PCR) experiments. They are made of a thin-walled plastic material that allows for efficient heat transfer and are available in different sizes to accommodate various sample volumes.
Uses of Centrifuge Tubes Centrifuge tubes are used in a variety of scientific and medical applications, including:
- Separation of Blood Components: Centrifuge tubes are commonly used in medical laboratories to separate the various components of blood, including red and white blood cells and plasma.
- Cell Culture: Centrifuge tubes are used in cell culture applications to isolate cells from their growth medium or to pellet cells after harvesting.
- DNA and RNA Extraction: Centrifuge tubes are used in DNA and RNA extraction protocols to separate nucleic acids from other cellular components.
- Protein Purification: Centrifuge tubes are used in protein purification protocols to separate proteins based on their molecular weight.
Best Practices for Handling and Storing Centrifuge Tubes Proper handling and storage of centrifuge tubes are crucial to ensuring accurate and reproducible results. Here are some best practices to follow:
- Label Tubes: Always label your centrifuge tubes with the sample name, date, and any other relevant information. This will help you keep track of your samples and avoid confusion.
- Store Tubes Properly: Store your centrifuge tubes in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. This will help to prevent damage to the tubes and protect the integrity of your samples.
- Use Appropriate Centrifugation Conditions: Always use the appropriate centrifugation conditions for your specific application, including the correct speed and duration of centrifugation.
- Check Tubes for Damage: Before using a centrifuge tube, always check it for cracks, chips, or other damage that could affect its performance.
- Dispose of Tubes Properly: After using a centrifuge tube, dispose of it properly according to your laboratory’s guidelines. This may include autoclaving or disposing of it as hazardous waste.
In conclusion, centrifuge tubes are an essential tool in scientific and medical laboratories. They are available in a variety of types and designs, each suited to specific applications. Polypropylene and glass tubes are the most common types, while microcentrifuge, conical, and PCR tubes are used for specialized applications. Centrifuge tubes are used for various purposes, including separating blood components, isolating cells from growth medium, extracting DNA and RNA, and purifying proteins. To ensure accurate and reproducible results, it is essential to handle and store centrifuge tubes properly, label them appropriately, and dispose of them correctly. By following best practices, scientists and medical professionals can maximize the efficiency and accuracy of their centrifugation protocols.
It is also essential to select the appropriate centrifuge tube for a particular application. For example, glass tubes are preferred when optical clarity is required, while polypropylene tubes are more suitable for general-purpose applications. Similarly, conical tubes are useful when separating a solid or semi-solid material from a liquid, while microcentrifuge tubes are ideal for low sample volumes.
When handling centrifuge tubes, it is crucial to avoid damaging them, as this can affect the integrity of the sample and the accuracy of the results. It is also important to use the appropriate centrifugation conditions, including the correct speed and duration of centrifugation, to ensure that the sample is separated efficiently and accurately.
In addition to handling and storing centrifuge tubes properly, it is also essential to follow safety protocols when working with them. This includes wearing appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves and safety glasses, and following the guidelines for handling and disposing of hazardous materials.
In summary, centrifuge tubes are an essential tool for scientific and medical laboratories, used to separate materials based on their density. There are various types of centrifuge tubes available, each suited to specific applications, and it is essential to select the appropriate tube for a particular purpose. Proper handling and storage of centrifuge tubes, as well as following safety protocols, are crucial to ensuring accurate and reproducible results. By following best practices, scientists and medical professionals can maximize the efficiency and accuracy of their centrifugation protocols and produce reliable and meaningful results.

 10ml measuring Cup
10ml measuring Cup 100 ml scaled Specimen Cup
100 ml scaled Specimen Cup 200 ml Sterile Specimen Cup
200 ml Sterile Specimen Cup 30 ml Specimen cup
30 ml Specimen cup 60 ml Specimen cup
60 ml Specimen cup Polypropylene Titration cup 100ml
Polypropylene Titration cup 100ml 200 ml Specimen cup
200 ml Specimen cup Milk test tubes
Milk test tubes 24 hour Urine Collection Containers
24 hour Urine Collection Containers Urine Specimen Cups
Urine Specimen Cups Urine Collection Cup + Cap with Two Openings
Urine Collection Cup + Cap with Two Openings Urine Collection Container - Vacutainer
Urine Collection Container - Vacutainer QuadLoop 1 uL & Needle end
QuadLoop 1 uL & Needle end QuadLoop 10 uL & Inoculating needle end
QuadLoop 10 uL & Inoculating needle end QuadLoop 10 uL & Sphere end
QuadLoop 10 uL & Sphere end QuadLoop 1uL & Sphere end
QuadLoop 1uL & Sphere end QuadLoop Needle & Sphere end
QuadLoop Needle & Sphere end Sterile Cell spreaders, Drigalski spatulas
Sterile Cell spreaders, Drigalski spatulas 15 ml Centrifuge Tubes
15 ml Centrifuge Tubes 30 ml Transparent PS Tubes
30 ml Transparent PS Tubes 50 ml Centrifuge Tubes
50 ml Centrifuge Tubes Petri dishes 50 mm (55x14.2)
Petri dishes 50 mm (55x14.2) Petri dishes PS 90 mm diameter (90X15)
Petri dishes PS 90 mm diameter (90X15)