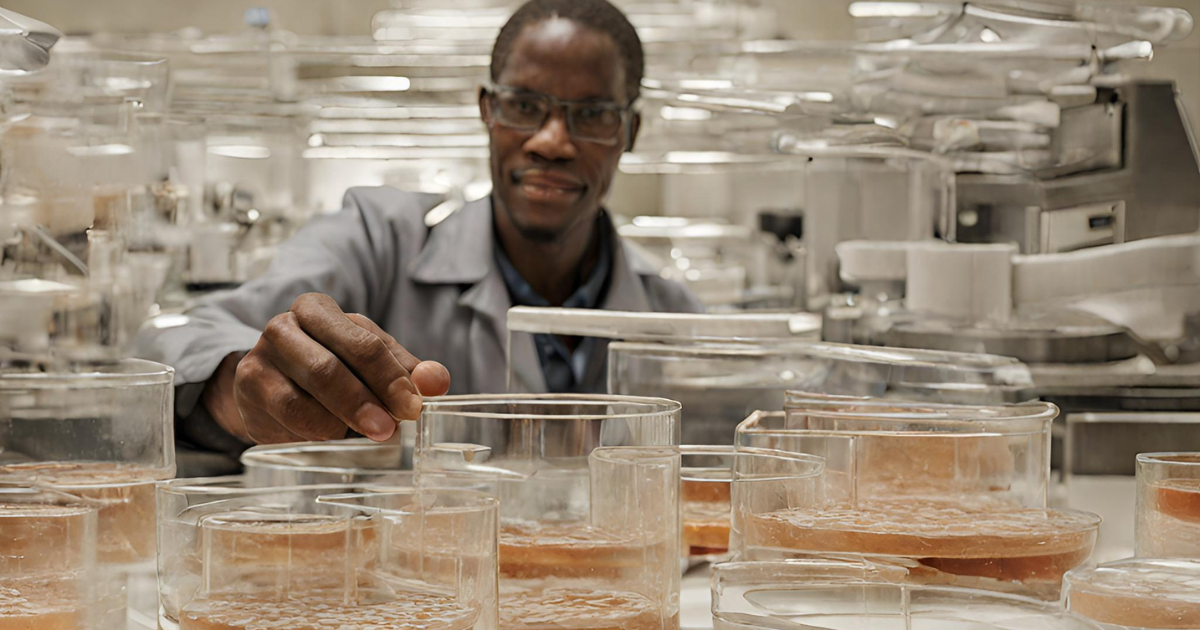
Petri dishes, those unassuming shallow containers found in laboratories worldwide, have played an instrumental role in fostering scientific innovation. In South Africa, these simple tools have been at the forefront of pioneering research and advancements in various fields. This article explores the multifaceted impact of petri dishes in South Africa’s scientific landscape, emphasizing their contributions to microbiology, healthcare, and biotechnology.
- Microbial Diversity and Environmental Studies:
South Africa’s unique geography and biodiversity have made it a hub for studying microbial life. Petri dishes have been indispensable in cultivating and analyzing diverse microorganisms found in different ecosystems, aiding in the preservation of the country’s natural heritage and contributing to global environmental research. - Public Health and Disease Control:
The country has faced significant public health challenges, including the HIV/AIDS epidemic and tuberculosis. Petri dishes have been instrumental in diagnostic testing, tracking disease outbreaks, and developing strategies for disease control and prevention, showcasing South Africa’s commitment to improving healthcare outcomes. - Pharmaceutical and Biotechnological Innovation:
Petri dishes serve as incubators for biotechnological breakthroughs. South African researchers have harnessed their power for genetic engineering, pharmaceutical development, and the creation of bio-based products. These advancements have bolstered the nation’s biotechnology sector and economic growth. - Collaborative Endeavors and International Partnerships:
South Africa actively collaborates with global partners, sharing expertise, research findings, and resources. Petri dishes have been a common language for scientific cooperation, facilitating joint projects that address critical challenges like infectious diseases, agriculture, and climate change. - Empowering Local Talent and Capacity Building:
South Africa recognizes the importance of nurturing homegrown scientific talent. Initiatives and educational programs have been established to train the next generation of researchers, equipping them with the skills to use petri dishes as a tool for exploration and innovation. - Guide to Centrifuge Tubes:
Researchers in South Africa also rely on various tools and equipment to complement their work with petri dishes. One essential tool is the centrifuge tube. To learn more about its importance and usage, you can refer to our article, “Guide to Centrifuge Tubes,” which explains their role in sample separation and preparation. - Preventing Air Contamination During Inoculation:
When working with petri dishes, preventing air contamination is crucial. Scientists use specialized techniques, such as using an inoculating loop, to ensure the purity of cultures. To understand how air contamination is prevented when using an inoculating loop, read our article on the topic, which provides valuable insights into this critical aspect of laboratory work. - Future Prospects and Challenges:
While South Africa has made remarkable strides in utilizing petri dishes for scientific advancement, it still faces challenges such as resource constraints and the need for sustained investment in research and development. Nevertheless, the nation’s determination and resourcefulness continue to drive progress in scientific endeavors.
Petri dishes symbolize South Africa’s commitment to science and innovation. They have facilitated groundbreaking research in microbiology, healthcare, and biotechnology, enriching the nation’s scientific heritage and contributing to global knowledge. As South Africa continues to embrace these unassuming yet powerful tools, the future holds exciting opportunities for scientific discovery and technological innovation, benefiting not only the nation itself but the global scientific community as well.

 10ml measuring Cup
10ml measuring Cup 100 ml scaled Specimen Cup
100 ml scaled Specimen Cup 200 ml Sterile Specimen Cup
200 ml Sterile Specimen Cup 30 ml Specimen cup
30 ml Specimen cup 60 ml Specimen cup
60 ml Specimen cup Polypropylene Titration cup 100ml
Polypropylene Titration cup 100ml 200 ml Specimen cup
200 ml Specimen cup Milk test tubes
Milk test tubes 24 hour Urine Collection Containers
24 hour Urine Collection Containers Urine Specimen Cups
Urine Specimen Cups Urine Collection Cup + Cap with Two Openings
Urine Collection Cup + Cap with Two Openings Urine Collection Container - Vacutainer
Urine Collection Container - Vacutainer QuadLoop 1 uL & Needle end
QuadLoop 1 uL & Needle end QuadLoop 10 uL & Inoculating needle end
QuadLoop 10 uL & Inoculating needle end QuadLoop 10 uL & Sphere end
QuadLoop 10 uL & Sphere end QuadLoop 1uL & Sphere end
QuadLoop 1uL & Sphere end QuadLoop Needle & Sphere end
QuadLoop Needle & Sphere end Sterile Cell spreaders, Drigalski spatulas
Sterile Cell spreaders, Drigalski spatulas 15 ml Centrifuge Tubes
15 ml Centrifuge Tubes 30 ml Transparent PS Tubes
30 ml Transparent PS Tubes 50 ml Centrifuge Tubes
50 ml Centrifuge Tubes Petri dishes 50 mm (55x14.2)
Petri dishes 50 mm (55x14.2) Petri dishes PS 90 mm diameter (90X15)
Petri dishes PS 90 mm diameter (90X15)